Asian Needle Ant (Brachyponera chinensis)
Updated on
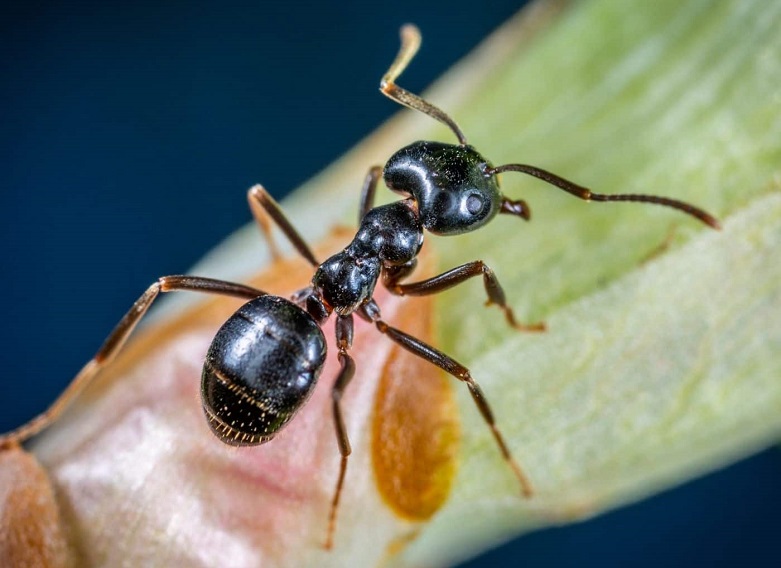
29/11/2022The Asian needle ant, as the name suggests, is a native of Asia. This medium to small-sized ant has rapidly spread in the US. It has a painful sting that can trigger an allergic reaction in humans.
Scientific Classification
- Order: Hymenoptera
- Family:Formicidae
- Subfamily:Ponerinae
- Genus:Brachyponera
- Species:B. chinensis
Conservation Status
Description
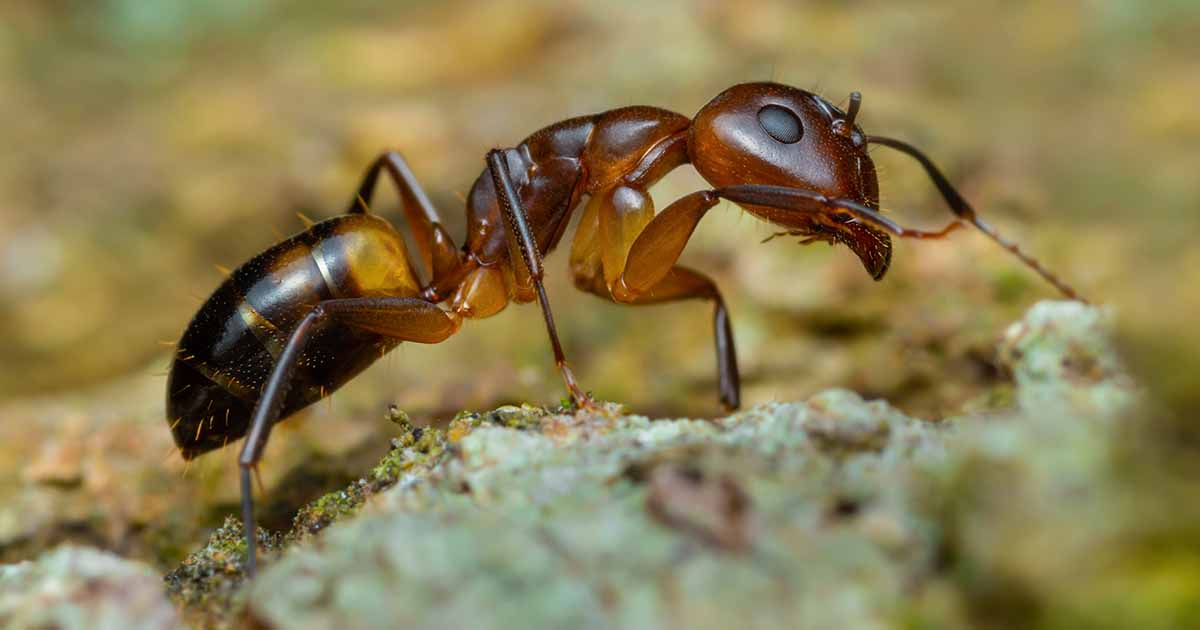
The size of the Asian needle ant workers and queens is 1/5-inch (5.0-6.0 mm). Both look similar with their long and slender bodies of dark brown to black color and light brown to orange-ish legs and mandibles.
Distribution: Japan and other parts of Asia, United States (in Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Kentucky, and Virginia).
Habitat: Trees, under rocks, collections of wood (like firewood); common, moist, and dark areas in the wild and also indoors, around electrical wires.
Do They Bite/Sting: Yes.
Lifespan: A few days for males, several years for queens, and a few weeks to several months for workers.
Predators: Birds, beetles, flies, caterpillars, spiders, snails, snakes, and lizards.
Behavior and Characteristics
Diet
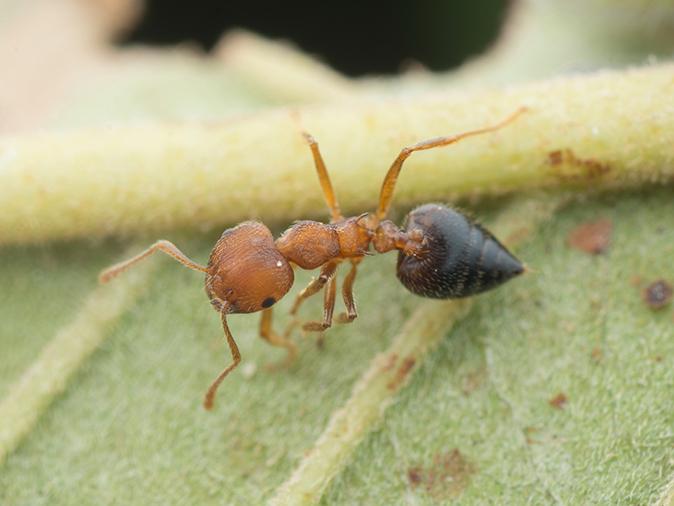
Though Asian needle ants prefer termites, they have been found scavenging on various arthropods and invertebrates like crickets, crane flies, earthworms, cockroaches, collembolans (“springtails”), beetles, grasshoppers, centipedes, spiders, and other dead organisms. They also direct colony members to sources of sugar such as jam and scavenges food particles from trash bins.
Defense Mechanism
A good thing about the species is that they are not much aggressive and try to flee upon encountering humans. Stinging is their last resort if they feel threatened.
Nest-building
The ant prefers nesting in dark and damp areas of soil below logs, stones, debris, and stumps. They also build nests on man-made structures like inside pavement crevices and around sprinkler systems.
Their colonies are polydomous, meaning one colony is made of several nests. They are also polygynous, as one colony can have multiple queens at the same time. The colony territories may span several nests at the base of one tree to several nests in a few closely placed logs. A colony can have less than 50 (as in a single nest site) to more than 50,000 (as in multiple adjacent nest sites) individuals.
Comparison with Similar Species
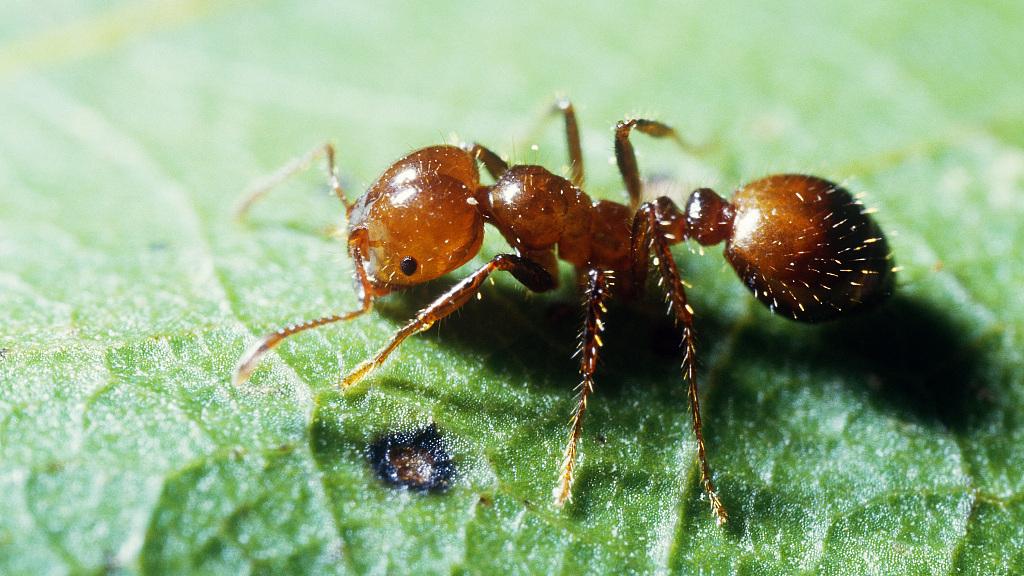
Fire Ant
Fire ants are more aggressive than Asian needle ants.
Getting Rid of Asian Needle Ants
Its negative ecological impact on biodiversity (caused by its wiping out of native ants and termites), infestation of homes, and harmful effects on human health through its sting-induced severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) have made the pest a cause of grave concern. Protein-based insecticide baits can be used to control them.
Source
cabidigitallibrary.org, ibe.upf-csic.es, journals.plos.org, antwiki.org